GABA supplements are popular because low levels of GABA can contribute to anxiety, mood disorders, restlessness, and more.
If this sounds like you, then you may naturally gravitate towards the thought of taking GABA supplements to improve your well-being.
However, understanding this substance and how it works to provide many beneficial effects can help distinguish whether GABA is the problem or solution in your unique situation.
Before we dive in, let’s look at what GABA does, what is it, and why is it important?
Contents
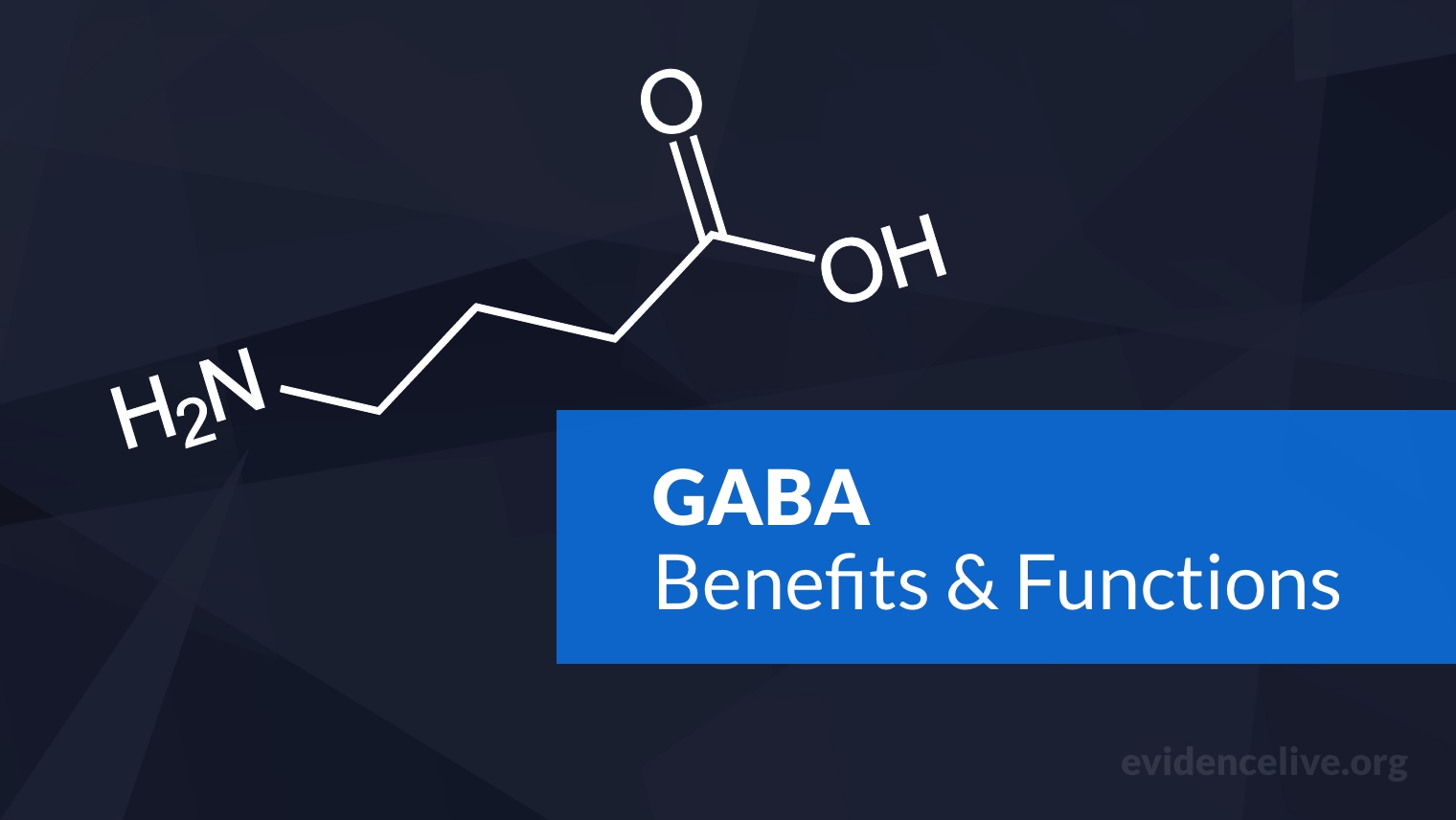
What is GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid)?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an amino acid and the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter that sends specific brain signals across nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
The compound binds to the GABA receptors to offer many essential benefits to the brain and body. GABA plays a vital role in anxiety, fear, and stress.
The binding activity to the GABA-A receptor and the affinity at GABA-B receptors allow modulation and blocked impulse between nerve cells, reducing anxiety and promoting a calming effect.
The nerve cells can be activated when the body does not have sufficient stimulation at the GABA receptors. When this occurs, existing conditions can worsen.
For example, low levels of GABA correlate with seizure disorders, mood disorders, anxiety, Parkinson’s disease, and more.
Some medications influence GABA levels to provide relaxation, pain relief, reduce anxiety and stress, lower blood pressure, and improve sleep.
For example, GABA modulating drugs like barbiturates, anti-seizure medications, anesthetics, anticonvulsants, and benzodiazepines influence GABA activity and modulate GABA signaling.
Gabapentin is another medication that increases GABA and is used to treat neuropathic pain, seizures, and muscle pain.
The amino acid is also found naturally in green and black tea and fermented foods. Also, some foods can increase GABA directly or indirectly, including whole grains, spinach, broccoli, tomatoes, citrus, soy, lentils, beans and nuts, and some fish.
However, sometimes food is not enough to raise GABA amounts, and nootropic supplements or other dietary supplements are the choices.
What Does GABA Do?
Whereas an excitatory neurotransmitter will encourage nerve action potentials, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, like GABA, will inhibit neurons and make them less likely to fire and lessen the relevant activity in the central nervous system.
When an action potential arrives at the axon terminal of a GABAminergic neuron, GABA releases into the synaptic cleft. The GABA binds to the post-synaptic receptors, which open chloride ion channels.
The action at the GABA receptors is a rush of negatively charged chloride ions into the receiving neuron that becomes more negative inside the cell membrane. This means that it will be much less likely to fire an action potential.
All of this occurs within milliseconds, but the GABA will slowly unbind to the receptor so that the calmness lasts. However, this calming effect is only apparent with GABA in the brain.
In the spinal cord, the process influences sensory information integration. In turn, this helps with smooth muscle movements.
GABA also plays a role in the immune and endocrine systems and regulates the appetite, metabolism, complete gut health, and gastrointestinal function. It even helps to manage hormone levels and balance.
What Are The Benefits of GABA?
GABA modulation is essential for the normal functioning of the body and brain. Moreover, it offers a variety of beneficial effects that show the importance of adequate amounts.
Sleep
GABA activity interacts with the brain process to induce sleepiness. It allows us to relax both mentally and physically to properly drift off to sleep when bedtime arrives.
Research shows that low GABA is associated with poor sleep and insomnia. Therefore, commonly there are prescribed medications, like zolpidem, for sleep work by inducing increased GABA signaling (1).
Without sufficient GABA, the central nervous system remains active, which keeps us awake or, at the very least, disrupts our REM sleep patterns.
In addition, many people have trouble sleeping because of racing thoughts or anxiety, and this neurotransmitter can also reduce these symptoms to help you fall asleep faster.
GABA will also keep you asleep during the night so that you do not toss and turn or wake up after every sleep cycle.
This ensures that our brain has the time to process memories and other information that allows us to wake up feeling refreshed and energized.
Stress and Fatigue
If you have ever been stressed out for a long time, you know it can drain your energy and make you feel mentally and physically worn out.
This fatigue can lessen productivity, impact mental health, and cause our stress levels to continue to rise unimpeded.
However, when the GABA receptor has a sufficient bind from the molecules, our brain can deal with this stress and alleviate the symptoms associated with burnout.
When we can reduce stress, our mind and body receive the needed break from heightened brain activity. This can help us stabilize our mood and get our natural energy levels back.
GABA may even be beneficial for major depressive disorder by increasing energy levels and reducing stress’s strain on our brain (2).
The effects of GABA allow us to reduce stress without intoxication or reduced cognitive function since it is a natural neurotransmitter. It also acts with other neurotransmitters to keep stress in check while managing other mental, physical functions and processes.
Anxiety
Anxiety disorders make relaxation difficult because the body remains tightened up, even at bedtime or in times of low stress.
Many times, these negative effects are associated with meager amounts of GABA. Studies indicate increasing GABA can lower anxiety and help to promote adequate relaxation (3).
This is especially true when there is an optimal balance of GABA working alongside other neurotransmitters. With insufficient GABA, our bodies are on edge constantly, never giving us time to relax and destress.
This is the worst combination for those who have anxiety disorders that can lead to more symptoms like insomnia, rapid heart rate, difficulty breathing, and more.
GABA also helps with resilience to anxiety and stress. When we have enough, our neurons will not become overactive and cause us to have negative physical ailments that often coincide with anxiety and depression.
Increasing GABA activity can help benefit our overall mental and physical health by eliminating harmful, stressful thought processes and the symptoms that come with these feelings.
Cognitive Performance
While it is not a traditional type of nootropic, research suggests that GABA synthesis is associated with cognition and can improve mental status and performance (4).
There are a few reasons behind this benefit of GABA activity. Some of the cognitive benefits are direct, while others are indirect effects of chemical messengers.
When we are stressed out, especially for long periods, we can become tired and easily distracted from mental tasks. In the long term, this can lead to burnout and other negative effects on cognition.
As a mood stabilizer and anxiety-reducer, GABA eliminates the stress that can shackle memory, focus, and overall cognition.
In addition, one study shows that GABA supplementation can reduce fatigue and improve some beneficial cognitive traits by lowering cortisol. In these studies, the participants with increased GABA had better scores because they could concentrate and pay attention longer before fatigue set in.
They also had better processing abilities, and problem-solving functions increased with a plethora of mental tasks.
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure can contribute to several disease states and health problems, including an increased risk of heart disease in humans.
Some peer-reviewed studies show GABA may be good for high blood pressure, although more research is needed (5). The reasons behind this are varied, but it could partially be tied to the relaxing properties of the effects of GABA.
Some scientists discuss the reasoning behind this and conclude that GABA can dilate blood vessels. This can increase blood flow and relieve some of the pressure within the pathways.
While there is not enough research, some scientists have even hypothesized that this could increase blood flow and lead to healthier brain cells and overall cognitive and physical health.
In addition, the efficacy of taking GABA supplements may allow some benefits to the nervous system that could influence blood pressure indirectly.
For example, high blood pressure is associated with hyperarousal, which can correlate with stress, and the ability to relieve stress may also ease blood pressure.
Muscle Recovery
Most people don’t think to take a GABA supplement for the workout, but taking GABA supplements may benefit muscle recovery (6).
Researchers have shown that those who take GABA supplements daily had better recovery times, better muscle tones, and builds.
This may be because of the muscle relaxant and sedative properties of GABA, but it may also influence muscle tone and strength. It may even prevent injury because it allows for greater flexibility and movement that helps to create smooth movements and healthier muscle distribution.
Furthermore, there is also some evidence suggesting that GABA could boost the effectiveness of the body’s support systems that fight inflammation and pain (7).
The effects of GABA could trigger the slowing of inflammation because of communication with neurologic pain sites. Better communication and lower inflammation help in protecting muscle recovery and injury response.
What To Know About GABA Supplements?
If you want to increase brain GABA, you would probably first turn to it as a supplement. Usually, people use GABA supplements for sleep, cognition, stress, blood pressure, and mood improvement.
However, there are some things to keep in mind when determining which GABA supplements will be effective.
The best GABA supplements will readily cross the blood-brain barrier to support brain health. Unfortunately, many plain gamma-aminobutyric acid supplements do not consider this, and the supplement form will not have high effectiveness.
Another thing to keep in mind is the balance of other neurotransmitters. Therefore, many gamma-aminobutyric acid supplements contain or encourage you to use additional vitamin supplementation or combination with other nootropic herbs for the intended effects you desire.
Several herbs and food supplements can positively affect the GABA in your brain. For example, many people rely on 5-HTP to control the amounts of neurotransmitters. Vitamin B6 is another excellent choice that offers additional benefits as well.
Other natural herbs that influence GABA and synergize well with it. Chamomile is also an excellent choice to amplify the relaxing and sleep-inducing qualities. A good option for enhancing anxiety-fighting properties is St. John’s Wort.
One of the most popular nootropics to combine with GABA is the valerian root, improving sleep or anxiety.
Another recommendation it to take a supplement source of l-theanine that can provide better cognitive activity with a relaxed mindset. Doing this can help you achieve the results you want and make a significant difference in your well-being.
Dosage
While there are no exact dosages given by science for gamma-aminobutyric acid, there are some recommended amounts you can follow based on research and many other studies.
For sleep, cognition, stress, and anxiety, you will want to start at 100 mg. However, you may need 200 mg or even more for desired results.
On the other hand, the evidence shows that a microdose of as little as 10 mg may be enough for high blood pressure.
What Causes Low GABA Levels?
While there is no direct cause of low gamma-aminobutyric acid, some factors contributing to low GABA are genetics, certain diseases, long-term stress, lack of exercise, and poor diet. Consequently, GABA deficiency can contribute to several other conditions.
Some psychiatric conditions associated with low GABA include anxiety, depression, insomnia, and schizophrenia. Low GABA may also play a role in autism spectrum disorder (8).
Some physical ailments of low amounts include pyridoxine deficiency, hepatic encephalopathy, Huntington’s disease, dystonia, and muscle spasticity. Frequent seizures may be another sign of too little GABA.
Some of the common symptoms of low GABA include stress and anxiety, low mood, low energy, poor memory, difficulty concentrating, muscle pain, headaches, and insomnia.
Low GABA may also contribute to substance use disorder and the abuse of substances. In fact, alcohol and some other common drugs of abuse influence GABA.
You may also find that your symptoms get better when you try to increase GABA. There are several ways to increase GABA naturally that can be pretty effective for some people. While they may not all work, you may find one or two that have a beneficial effect.
Are There Any Side Effects of Too Much GABA?
While GABA can offer many benefits, there are possible side effects while having too much of it.
Potential side effects include numbness and tingling, especially in the extremities and mouth, drowsiness, nausea, lightheadedness, intoxication, hallucinations, and mood swings. It can also cause headaches or allergic reactions in some people.
There are some other things to keep in mind before GABA supplementation. For example, alcohol and other sedative drugs can increase GABA activity leading to negative interactions.
This can lead to respiratory depression and over-sedation. Therefore, be careful when taking GABA-modulating drugs.
Some medications like benzodiazepines affect gamma-aminobutyric acid. Therefore, taking GABA with these drugs may increase the risk of overdosing.
While medicine can reverse benzodiazepine intoxication, if it is not administered in time, the overdose could be fatal. If you experience any side effects, then you should decrease your dose to eliminate the negative feelings.
Some medical conditions may also have adverse interactions with some GABA supplements, and you should take caution before choosing GABA as a supplement. For your safety, it is always best to have a doctor provide medical advice.
Conclusion
Optimal GABA amounts in the brain and nervous system are crucial for many brain and body functions. The effect of low GABA or imbalance could be anxious thoughts, fatigue, poor sleep, prolonged stress, low mood, and more.
GABA acts as a chemical messenger that can promote relaxation and produce a sense of calm, and you may find that you feel better when you take a supplement that increases GABA.
However, some people find natural methods to help GABA supplements produce a better response because it protects GABA levels that are increased naturally.
Whether you suffer from low GABA or want to give your quality of life a boost, you may find that GABA helps you avoid stressful impulses and focus on work with a positive mindset.