A favorite among the biohacking community, phosphatidylserine is a popular nootropic with many benefits to boast.
It covers everything from cellular health and maintenance to preventing age-related mental decline and is crucial at every stage of life. Plus, it can help you perform well on a physical level as well.
So, if you have trouble remembering details or want to sharpen your mental skills, take a good look at the expansive list of phosphatidylserine benefits and how they may help you.
Contents
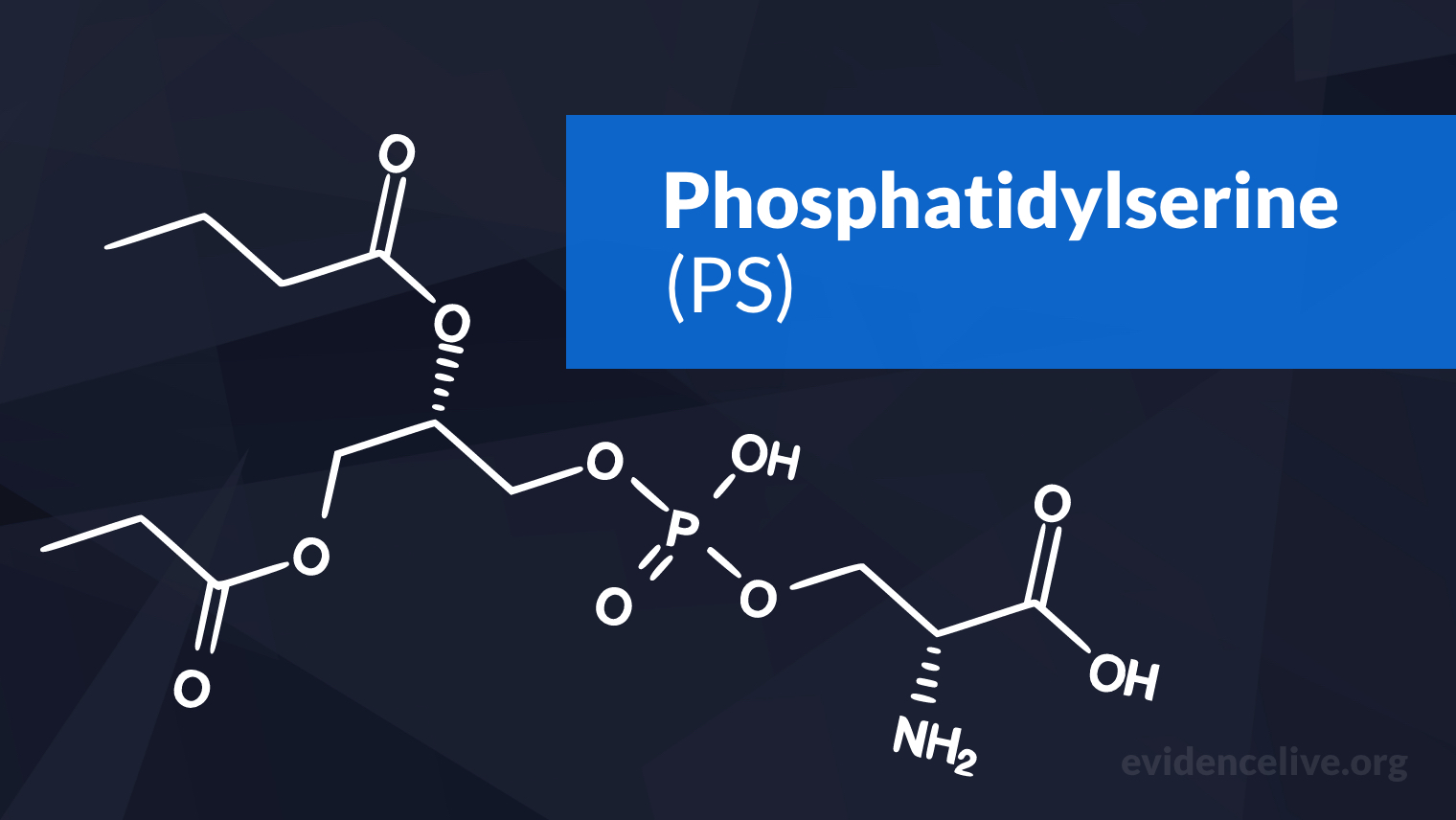
What is Phosphatidylserine (PS)?
Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid or fat present naturally in every cell in the human body and is found in notably higher concentrations in the brain.
In the brain, phospholipid phosphatidylserine (PS) is essential for optimally functioning brain cells and preserving cell integrity.
As people age, phosphatidylserine levels naturally decline, so restoring them becomes vital to keep up overall brain function, memory retention, and improve mood. It may also help slow cognitive decline and may even possibly prevent the progression of dementia.
But its health benefits are not restricted to the elderly only. Research on phosphatidylserine suggests it to be equally beneficial for optimizing mental performance in younger demographics as well.
Phosphatidylserine can be sourced from certain foods in the diet but may not be enough. So, your doctor may suggest supplements to meet the required demands.
How Does Phosphatidylserine Work?
Phosphatidylserine plays a role in normalizing what is known as the HPA axis. It refers to the stress-induced overstimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
The HPA axis serves as a means of phosphatidylserine communication between the brain and adrenal glands to maintain cortisol release in the body.
It has often been used in collaboration with other nutritional supports like phosphatidic acid or omega 3 fatty acids for better stress management (1).
Phosphatidylcholine vs. Phosphatidylserine: What’s The Difference?
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylserine (PS) are both phospholipids naturally present in all cells in the body, with the former attached to a choline particle. Both have been studied concerning brain health with phosphatidylcholine, supporting liver health, and keeping cholesterol readings in check.
However, their other functions and activities in the body vary.
Phosphatidylcholine is involved in acetylcholine production, which is important for memory and other bodily functions. It is also a source of choline and may be helpful in treating ulcerative colitis.
On the other hand, phosphatidylserine is equated more with brain-boosting benefits like orchestrating neurotransmitters in the brain, managing and preserving brain cell structure, and protecting against mental decline in old age.
What Are The Health Benefits of Phosphatidylserine?
Phosphatidylserine supplements seem to present health benefits that cover several issues from memory enhancement and ADHD management to depression and improved physical performance.
This makes it a versatile yet safe treatment option to consider for these conditions.
Memory Improvement
The most crucial function phosphatidylserine performs as a brain supplement is to provide structural support for brain cells. Not only does it help keep structural integrity intact, but it also aids their flexibility and fluidity.
Plus, phosphatidylserine manages neurotransmitters and receptors. It acts in a coordinating capacity to store, release, and oversee key brain chemicals and their corresponding receptors that affect memory, mood, and new learning.
These mechanisms are directly linked to brain health, where they improve memory, concentration and boost brain cell communication.
Aids In Cognitive Enhancement To Age-Related Decline
As a brain supplement, PS is also used as a raw material in creating new brain cells.
One of its most well-studied health benefits is to assist cognition to age-related degenerative diseases and concerns.
One study recruited people aged 55-75, administering PS supplementation for 12 weeks. At the end of the trial period, study results showed significant enhancement in memory scores.
Another study investigated how PS may benefit age-related brain fog in individuals between the ages of 50 and 75. Subjects were given 100mg PS or a placebo daily for 12 weeks. Study findings showed that the group taking phosphatidylserine supplements scored better on cognitive testing related to memory and learning (2).
Helps With Stress, Cortisol, and Depression
Phosphatidylserine may also signal for dopamine release, the neurotransmitter linked to feelings of motivation and mind-body coordination.
Some studies indicate that PS may well lower stress levels and improve mood. In a research study with young adults, taking 300 mg of phosphatidylserine seemed to benefit from feeling less stressed and experiencing a better mood (3).
The same kinds of benefits were also observed in other clinical trials with older adults where PS supplementation blunted cortisol spikes that typically occur with physical exercise (4).
Some preliminary studies also suggest that phosphatidylserine may lower depression in the elderly.
One such study found that a combination of PS and omega 3 fatty acids worked favorably for elderly adults who suffered from late-life depression.
Study participants had been unresponsive to antidepressant medications but saw an improvement in depression scale with PS supplementation (5).
Boosts Exercise Performance
Phosphatidylserine is of particular interest to athletes as recent research has shifted focus on its effects on athletic performance.
Once again, the HPA axis comes into play as chronically elevated stress hormones are linked to immune suppression, tissue breakdown, muscle damage, and muscle soreness.
Different studies with athletes using phosphatidylserine supplements have shown progress in increased exercise capacity, reduced ACTH and cortisol levels, less muscle soreness, and an improved perception of well-being when using the supplements (6).
Supplementation for athletic performance has also shown a lowering of creatine kinase activities in circulation, which is a generally accepted indicator of cell membrane damage and muscle fiber necrosis, 24 hours after exercise.
Other clinical trials show that phosphatidylserine when taken alongside caffeine and vitamins, may benefit mood and lower fatigue after exercising. However, it isn’t clear whether these benefits are from phosphatidylserine or other ingredients.
Helps Alzheimer’s Disease Symptoms
Because phosphatidylserine is active in restoring memory and learning-related neurotransmitters, it is considered a symptom management option for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Evidence is mixed with some studies showing positive implications while others don’t have much to offer for cognitive functioning.
For instance, earlier clinical trials with Alzheimer’s patients administered 300 mg of PS daily for 8 weeks, with results showing an improvement in overall well-being than others who took a placebo. Still, there were no gains in mental function tests (7).
In comparison, more recent research looked at both human and animal studies to see the effects of PS with Alzheimer’s disease.
The human research showed positive changes in vocabulary and picture matching scores, while the animal study exhibited reduced latency, lower acetylcholinesterase, and greater efficacy (8).
PS has also been considered a treatment for other forms of dementia, such as Parkinson’s disease, given its ability to increase dopamine in the system.
People with Parkinson’s disease exhibit a dopamine deficiency traced to a nerve cell disorder that produces this vital neurotransmitter.
In this respect, it is a promising compound for those seeking treatments for neurodegeneration.
Treats ADHD Symptoms
Another area of research is the effects of phosphatidylserine on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
ADHD is typically diagnosed in children with excessive inattentiveness, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness.
One 2014 study worked with children aged 4-14 diagnosed with ADHD. Study subjects were given a 200 mg dose daily for two months, with findings showing benefits to attention, impulse control, and memory (9).
A few slightly earlier studies looked at the effects of a PS-omega 3 fatty acids complex administered to children with ADHD, with findings showing a reduction in symptoms and improvements on the visual sustained attention aspect (10).
This evidence shows that PS, typically pigeonholed for elderly cognitive performance, can be effective for a much younger age group also.
And while ADHD is typically identified in childhood, it can also affect adults. Once again, phosphatidylserine can help to boost mental focus, mood, memory, and cognition by relieving stress through balancing hormones.
Improves Sleep Quality
People with intermittent sleep issues realize that their fragmented sleep is often anxiety and stress-related. When you find it hard to stop yourself from reacting to stressful situations, your body does what it’s designed to do, releasing more of the stress hormone cortisol.
Any HPA axis over stimulation that releases an excess of the stress hormone impacts the sleep negatively, leading to various sleep disturbances.
With its ability to manage cortisol release, phosphatidylserine can act as an effective antidote to let you rest soundly at night. Taking a supplement before bed can help restore out-of-whack hormones and calibrate cortisol in the body (11).
Enhances Other Brain Supplements
Phosphatidylserine can be used as a standalone nootropic or combined with others for a superior synergistic effect.
Ginkgo Biloba and phosphatidylserine make a formidable combination with each other to benefit healthy cognitive function.
This potent duo has been used in quality products that support mental acuity, memory, and general cognitive function. The combined benefits of phosphatidylserine for neuronal structure and function and ginkgo Biloba for improved blood flow result in excellent effectiveness for memory support, anxiety reduction, and calming the mind.
Another example is combining PS with curcumin for enhanced efficacy. While curcumin improves cerebral circulation, lowers inflammation, and boosts dopamine and serotonin production, it is not absorbed well by the body.
PS can resolve this issue by improving its bioavailability and making it more readily available.
Phosphatidylserine also works well with the fish oil omega 3 fatty acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Like PS, DHA is also present abundantly in the human brain, and any decrease in either ones’ level can lead to cognitive decline and impairment.
A research team studying brain aging identified that there was quite a difference in the plasma fat content of people with Alzheimer’s, mild cognitive impairment, and others with healthy brains.
Team members established that DHA and PS levels in both disease categories were less than that of healthy brains and that supplementation would be beneficial for people with Alzheimer’s.
How To Take Phosphatidylserine?
There are food sources of PS but may not be part of everyone’s diet, especially vegetarians. So, to reap its health benefits, many people decide to make it part of their nutrition via supplements.
Phosphatidylserine supplements are easy to purchase as capsules and tablets. The varying strengths of the supplements can be between 100 mg to 300 mg each.
A patented form of phosphatidylserine known as Sharp-PS is made from non-soy, non-GMO vegetable sources and may be a better option for those who are concerned about GMOs.
Dosage
The optimal dosage for PS supplementation will vary based on why you want to use the supplement.
As a general health supplement, you can take up to 300 mg of PS per day divided into 3 doses of 100 mg each.
Your doctor may advise you to follow a dosage of three 100 mg capsules every day for up to six months to benefit memory.
For Alzheimer’s treatment, between 300-400 mg of phosphatidylserine has been used daily in divided doses.
Athletes will benefit from a slightly higher dosage of 200-400 mg 15-30 minutes before exercise.
How Long Does It Take For Phosphatidylserine To Work?
Phosphatidylserine can easily cross the blood-brain barrier, when supplemented correctly, to become more bioavailable in the brain.
Most people report an enhancement in mental acuity and cognition within 15-30 minutes of taking phosphatidylserine.
Experts recommended taking a phosphatidylserine supplement about 30 minutes before bedtime to experience a good night’s rest. This gives the body sufficient time to break it down.
Athletes should do the same 15-30 minutes before training.
What Are The Dietary Sources?
Dietary phosphatidylserine can be sourced from food sources like meat, fish, krill oil, and soy lecithin.
However, the brain, liver, and kidneys of animals are considered the densest PS foods. Unfortunately, not many people include organ meats as diet foods they often consume, so they may need to supplement PS instead.
Vegetarians can include it in their diet through the intake of dairy products and vegetables.
Does Phosphatidylserine Have Side Effects?
Because phosphatidylserine is already present in the body, the brain and body recognize it as a natural substance. This is why PS, in supplement form, is tolerated so well without many risks. It is generally considered safe and mostly side-effect-free when used in supplemental form.
In its preliminary stages, PS was sourced from cow brains that questioned its safety profile, especially regarding mad cow disease.
Then followed a time when phosphatidylserine supplements were derived from cabbage and soy. This version of the PS supplement used soy lecithin in its manufacturing.
However, soy is still a potential allergen, so another option to consider is sunflower-derived phosphatidylserine.
Sunflower sourced phosphatidylserine supplements are GMO -free, non-allergenic, and have fewer safety concerns. It is generally considered the higher quality PS source.
Studies show that up to 600 mg of phosphatidylserine per day has been used for 12 weeks without being associated with any serious side effects.
FDA sourcing guidelines approve PS claims for its possible effectiveness in reducing the risk of dementia and cognitive dysfunction in the elderly.
Possible side effects may occur if used above the recommended 300mg daily dose. The most commonly reported side effects include an upset stomach or insomnia.
People using blood thinners are advised not to use phosphatidylserine.
The same goes for people using performance-enhancing drugs, ACHe inhibitors, antidepressants, anticholinergic drugs, or for any other health condition like dementia.
Since there can be interactions with drugs, let your doctor know before starting any supplementation.
Phosphatidylserine Limitations
Many of the clinical trials conducted on phosphatidylserine benefits have been done on PS soured from animal brains, which was then discontinued due to concerns with mad cow disease. As a result, phosphatidylserine supplements available now are primarily sourced from soy, cabbage, or sunflower.
While animal-derived PS has presented benefits in areas of memory enhancement for people with age-related memory loss, the same cannot be said of plant-derived PS. Information is still limited in how effective PS products from plant sources are compared to their animal-sourced counterparts.
Also, taking PS supplements for Alzheimer’s seems to work best in people with less severe symptoms, and some evidence shows that it may become less effective over time.
Conclusion
Phosphatidylserine supplements can help you get out of the rut of unproductivity, chronic stress, and the inability to focus.
With research-backed claims, these and other benefits will help you regain your focus, improve your memory, and preserve your cognitive functioning, letting you perform at peak mental levels.
So why not add a supplement to your diet regimen today?
FAQs
- How much phosphatidylserine should I take to lower cortisol?
Taking 800mg of animal-derived PS lowered cholesterol response by 30%. A similar dose of Sharp PS also reduced cholesterol response to intensive training by 20%.
- Does phosphatidylserine make you sleepy?
Phosphatidylserine calms the mind by managing hormone levels and can be helpful for a good night’s rest.
- Does phosphatidylserine increase testosterone?
There is mixed evidence that PS can increase testosterone. More research is needed to establish whether it can enhance testosterone levels.